The most common nutrient deficiencies among college students and some of the steps you need to take during your academic life to ensure that you attain the best results despite the challenges.
Busy schedules, academic pressures, and unhealthy eating habits contribute to nutrient deficiencies among college students. College students may experience nutrient deficiencies because they prioritize convenience and affordability regarding meal choices.
Prioritizing convenience and affordability over nutritional value can seriously affect a student’s health, academic performance, and overall well-being. The good thing is that by creating and raising awareness of the various health problems among college students, individuals can develop practical solutions that will enable students to prioritize their health and work towards achieving their academic objectives.
Most importantly, students who have difficulty completing their research papers and essays for unavoidable reasons can always request help from reputable writing enterprises like Peachy Essay. That way, you will have ample time to handle other important aspects of school. This article will discuss nutrient deficiencies common among college students.
Vitamin D Deficiency
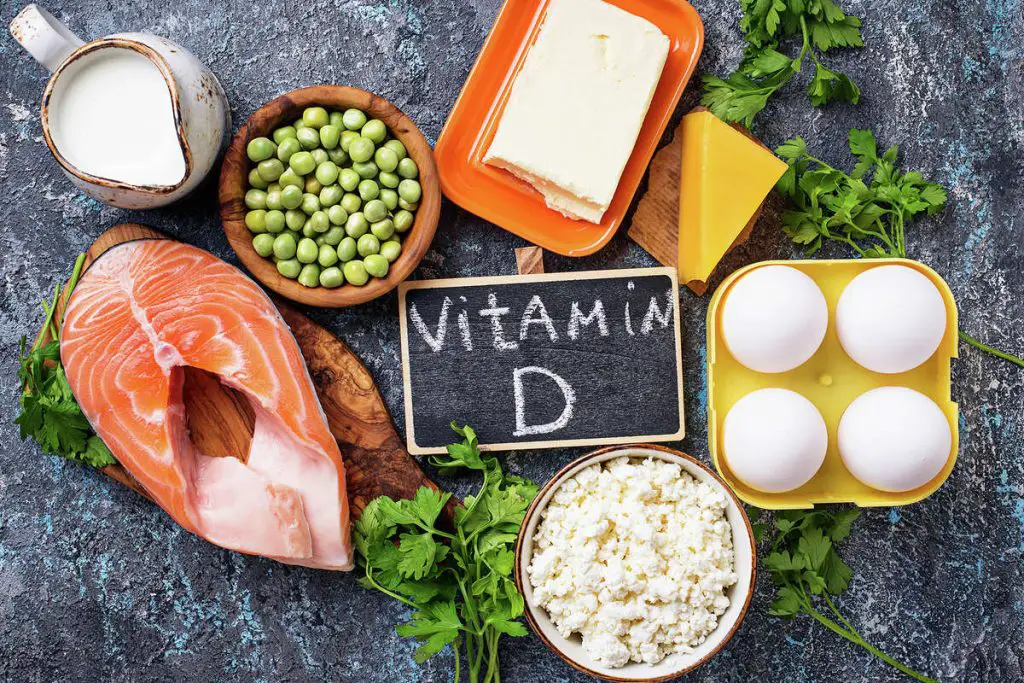

College students’ prolonged stay indoors studying or in classrooms increases their likelihood of vitamin D deficiency due to inadequate exposure to sunlight. Calcium absorption and bone health require Vitamin D.
When there is a shortage of vitamin D; bones can become fragile, leading to a higher propensity for fractures alongside several other health concerns such as respiratory infections, cardiovascular diseases, and depression. Students should be educated on preventing incidents or illnesses caused by a lack of vitamin D in the body.
Iron deficiency
Iron deficiency anemia, a result of a diet low in iron-rich foods, can make you feel dizzy or lightheaded.
Not eating enough iron-rich foods like red meat, beans, and leafy greens can cause college students to develop iron deficiency anemia. Iron deficiency can bring about fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and other health problems.
Dizziness or light-headedness can be caused by iron-deficiency anemia as well.
Calcium Deficiency

It is believed that calcium may aid individuals in preventing cancer, diabetes and high blood pressure. Strong bones and teeth require calcium.
Consuming insufficient calcium-rich foods, like milk, yogurt, cheese, and leafy greens, may lead college students to develop brittle bones and teeth. Insufficient calcium intake increases the probability of osteoporosis, which causes brittle and weak bones.
Maintaining strong bones and building them requires adequate calcium intake. The proper function of your heart, muscles, and nerves also requires calcium.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
The production of red blood cells and proper nervous system function require Vitamin B12.
A vegetarian or vegan diet may lead college students to have inadequate vitamin B12, mostly found in animal products. Nerve tissue health, brain function, and red blood cell production require Vitamin B12; inadequacy may result in numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, fatigue, or weakness.
The production of red blood cells, nerve tissue health, and brain function rely heavily on it. In essence, it is true to state that the vitamin significantly aids in strengthening nerve tissue, enhancing brain functioning, and stimulating red blood cell production.
Folate Deficiency
Folate can aid in preventing congenital disabilities and producing red blood cells. It is useful in averting significant congenital disabilities of the baby’s brain (anencephaly) and spine (spina bifida). The neural tube forms the early brain and spine, which can be affected by inadequate folate intake. The deficit of folate-rich foods may trigger folate deficiency anemia causing fatigue, weakness, irritability, and other health issues.
Magnesium Deficiency
Including heart rhythm regulation and bone formation, magnesium is key for many essential body functions. Consuming enough nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy greens can lead to magnesium deficiency in college students. Muscle cramps, an irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure, and other health concerns can arise from insufficient magnesium intake. To ensure that you remain healthy, it is paramount that you consume good foods.
Zinc Deficiency

It is vital to note that a healthy immune system, wound healing, and DNA and protein synthesis rely on Zinc. Red meat, poultry, seafood, and beans are excellent sources of zinc that college students need in order to prevent zinc deficiency. Insufficient zinc intake may weaken immunity and slow wound recovery and other health issues.
Vitamin C Deficiency
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in good immunity, collagen development, and iron uptake. Broccoli and bell peppers are some of the vitamin C-rich foods that college students should consume to avoid vitamin C deficiency. The lack of vitamin C in one’s diet may cause weakened immunity, insufficient wound healing, and various other health concerns.
Omega-3 fatty Acid Deficiency
A healthy brain and heart require omega-3 fatty acids. Insufficient consumption of omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds could leave college students vulnerable to deficiencies. Insufficient consumption of omega-3 can cause cognitive impairment, depression, anxiety, and increased heart disease.
Fiber Deficiency
An individual could be asking themselves a question such as How does fiber affect the body? Fibre, also known as roughage, when consumed in large quantities, is strongly linked to a lower risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and bowel cancer. Choosing fiber-rich foods can generate a feeling of fullness, in addition to boosting digestive health and preventing constipation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the challenges faced by college students in balancing academics and social life result in widespread nutrient deficiencies. College students’ physical and mental health can be seriously impacted by the ten nutrient deficiencies discussed, like vitamin D, iron, calcium, vitamin B12, folate, magnesium, zinc, vitamin C, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber.
College students can prevent and treat nutrient deficiencies by incorporating more nutrient-rich foods into their diet and taking supplements if needed. College students may experience nutrient deficiencies because they prioritize convenience and affordability when it comes to meal choices.
Prioritizing convenience and affordability over nutritional value can severely affect a student’s health, academic performance, and overall well-being. Moreover, giving importance to getting sufficient sleep, exercise, and stress relief can also back up total wellness and fitness. It is crucial for college students to prioritize their health and nutrition.