Alcoholism is a serious disease that affects millions of people all over the world. One of the main symptoms of alcoholism is cravings for alcohol.
People often wonder what causes these cravings, and what happens in the brain when they occur, even for things like chocolate.
In this blog post, we will explore alcoholism cravings in depth. We will discuss why people crave alcohol, what happens in the brain when they do, why people relapse, and how people can reduce their cravings.
Tell me the signs of alcoholism
There are many indications of alcohol abuse. However, making a real life assessment can be difficult because often people are caught up in self-deceit. Here are some of the common signs of alcoholism:
- Losing interest in activities that used to bring joy
- Avoiding friends and family
- Hiding alcohol
- Feeling guilty after drinking
Needing to drink more to feel the same effectsWhen three or more signs are matching your experiences, please seek help, as your symptoms match the criteria for Alcohol Use Disorder, more commonly known as alcohol addiction.
The sooner alcoholics become aware of their issue, the better they are treated and the more progress in life they make.What are alcoholism cravings?
Alcoholism cravings are an intense desire to consume alcohol. This can be triggered by certain cues, such as seeing a liquor store or bar, smelling alcohol, or even thinking about drinking.
For people with alcoholism, these cravings can be very hard to resist. In some cases, they may lead to relapse even if someone has been sober for a lengthy time.
Why do people crave alcohol?

There are several theories as to why people with alcoholism crave alcohol. One theory is that it is a form of self-medication.
People with alcoholism may crave alcohol because it helps to numb their emotions and make them feel better.
Another theory is that alcoholism is a form of addiction. Like other drugs, alcohol can cause changes in the brain that lead to cravings and addiction.
What happens in the brain when someone craves alcohol?
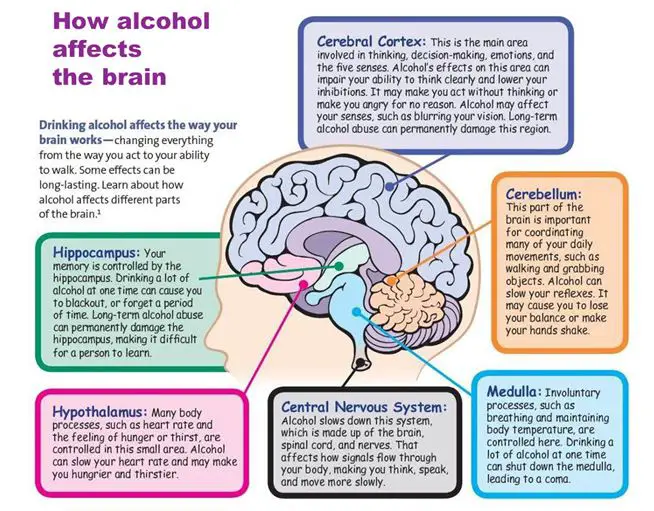
When someone with alcoholism sees a cue or thinks about drinking, there is a change in the brain.
The amygdala, which is the part of the brain responsible for emotional responses, becomes activated. This leads to a desire to drink alcohol.
Why? The amygdala scans the environment for danger. While you’re probably safe, the amygdala interprets stress as danger, and who isn’t stressed these days?
So, the amygdala knows alcohol helps you relax from stress, so it activates in this sense.
At the same time, the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making and impulse control, becomes less active.
Most importantly, when you crave alcohol, your brain is releasing a chemical called dopamine. This chemical is responsible for the pleasurable sensations you feel when you drink.
When you drink, your brain releases large amounts of dopamine, which creates a feeling of pleasure, and being carefree.
Over time, your brain becomes desensitized to the effects of dopamine and needs more and more alcohol to achieve the same effect. This is what leads to addiction and alcoholism.
Euphoric Recall and Appetitive Urges
Euphoric recall means that you remember the pleasant sensations you felt when you were drinking and you want to experience them again.
Appetitive urges are the physical cravings you feel for alcohol. These can be triggered by certain sights, smells, or thoughts that remind you of drinking.
Both of these mechanisms are controlled by dopamine in the brain and can lead to alcoholism cravings.
Internal signals that trigger memories can be thoughts, emotions, or physical sensations.
External signals that trigger memories can be people, places, things, or even songs.
These triggers cause the release of dopamine in the brain, which leads to cravings for alcohol.
Likewise, memories that trigger alcohol withdrawal can cause craving for alcohol.
Some studies also show that alcohol exposure can stimulate the salivary response of alcoholics, even when the alcohol is not taken as a drink.
Why do people repeatedly relapse?
Relapse is defined as a return to drinking after an extended period of sobriety. It is a very common occurrence in alcoholism, and there are many reasons why it happens.
Some people relapse because they are not ready to give up drinking. Others may relapse because they have not dealt with the underlying issues that led to their alcoholism in the first place.
People often relapse because they are trying to cope with negative emotions like anxiety, or depression. Drinking alcohol numbs these feelings and gives people temporary relief from their troubles.
However, this relief is only temporary, and it is quickly followed by feelings of guilt, shame, and regret.
Still others may relapse because they are trying to cope with a stressful life event and turn to alcohol as a way to cope. No matter the reason, relapse is a serious problem that can be difficult to overcome.
Overall, this cycle can be difficult to escape. After so many times attempting to quit but not actually doing so, often people believe they have no choice in their drinking habits. They can see and admit their alcohol dependence, but are unable to stop their alcohol abuse.
Strangely enough, the pattern is very similar to binge eating, which is why I wrote this post!
Indeed, the word “binge” originates from bingeing on alcohol!
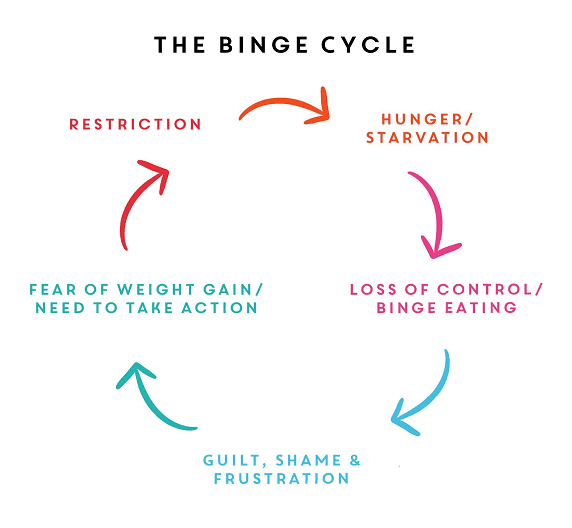
The role of craving in relapse
Some experts believe environmental factors are responsible for relapse more than physiological urges.
For example, if someone is in a situation where they are exposed to alcohol (such as being at a party), they may be more likely to relapse than someone who is not in that situation.
However, other experts believe that craving plays a more significant role in relapse. They believe that people who are trying to quit drinking are more likely to relapse if they experience strong cravings for alcohol.
Asa noted above, cravings can be triggered by many different things, including stress, anxiety, boredom, and depression. They can also be triggered by certain sights, smells, or thoughts that remind you of drinking.
High risk situations
Being aware of high risk situations is particularly important for quitting any addiction, including food and certainly alcohol.
High risk situations are those where there is a strong temptation to use, and/or where it would be very difficult to resist the urge to use.
Some examples of high risk situations for alcoholism include being around people who are drinking, being in places where alcohol is served, or seeing advertisements for alcohol.
How to reduce cravings
If you are trying to quit drinking or other forms of substance abuse, there are many things you can do to reduce your cravings for alcohol or substances.
First, it is important to avoid high-risk situations as much as possible, especially ones that explicitly involve drinking. If you cannot avoid them completely, try to limit your exposure to them.
Second, try to identify your triggers and find alternative activities that can help you cope with them. For example, if you usually drink when you are bored, try to find something else to do that is more stimulating.
Third, it is important to develop a support system of friends or family members who can help you stay on track. Seek professional help if you feel like you cannot overcome your cravings on your own.
Fourth, one of the most effective methods is through medication.
There are several medications that have been shown to be effective in reducing cravings. These include naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram.
Naltrexone is an opioid receptor antagonist that blocks the effects of alcohol in the brain. Acamprosate is a GABA agonist that reduces cravings by reducing withdrawal symptoms. Disulfiram is an aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor that makes people feel sick if they drink alcohol while taking it.
Fifth, another effective method for reducing cravings is through therapy. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that has been shown to be effective in treating alcoholism. CBT helps people identify their triggers and develop coping strategies to deal with them.
There are also many self-help groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous, that can provide support and guidance to people who are trying to quit drinking. Visit Abbey Care Foundation for more information about Alcoholics Anonymous
If you or someone you know is struggling with alcoholism, there are many resources available to help. Alcoholism is a serious problem, but it is one that can be overcome with the right treatment and support.
Lifestyle changes to support recovery
Self-care is essential. Alcoholism takes a toll on your body, so it’s important to take care of yourself physically.
This means eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly. It also means avoiding other substances that can worsen your condition, such as drugs and tobacco.
In addition to taking care of your physical health, it’s also important to take care of your mental health. This means managing stress in healthy ways and seeking professional help if you are struggling with depression or anxiety.
Meditation, or even simple walks outside or in nature can be great for your mental health.
Take on a hobby, like cooking or even playing chess!
Alcoholism is a serious problem, but it is one that can be overcome with the right treatment and support. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcoholism, there are many resources available to help.
Does alcohol cause food cravings?
Some researchers believe alcohol stimulates the brain hypothalamus and stimulates appetite. A recent study showed alcohol may stimulate neuron re-activation in brains triggered by hunger.
The study authors say this could be one reason why people who drink heavily eat more and are at a higher risk for obesity.
Other studies have found that people who drink before meals tend to eat more than those who don’t drink. And, alcoholics often crave high-calorie, fatty foods. So, it’s likely that alcohol increases food cravings and contributes to weight gain.
If you’re trying to lose weight or manage your weight, it’s best to avoid drinking alcohol altogether. If you do drink, make sure to do so in moderation and try to limit your intake of high-calorie foods while you’re drinking.
What does craving alcohol feel like?
The feeling of craving alcohol is different for everyone. Some may feel anxious, jittery, or irritable. Others may have trouble sleeping or concentrating. And some people may just have a general sense of unease or discomfort.
What is common to every person’s experience is a beginning, a middle and an end to the craving.
The beginning of the craving may be triggered by a thought, an emotion, or even a physical sensation. The middle is when the craving intensifies and you start to feel like you need to drink. The end is when you either give in to the craving and drink, or find a way to distract yourself or ride it out until it passes.
Alcoholism Craving – Summary
Alcoholism is a serious problem that can be overcome with the right treatment and support. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcoholism, there are many resources available to help.
There are also lifestyle changes you can make to support your recovery. Taking care of your physical and mental health is essential for overcoming alcoholism.
For more info about food cravings, and what they mean specifically, see this food chart here.